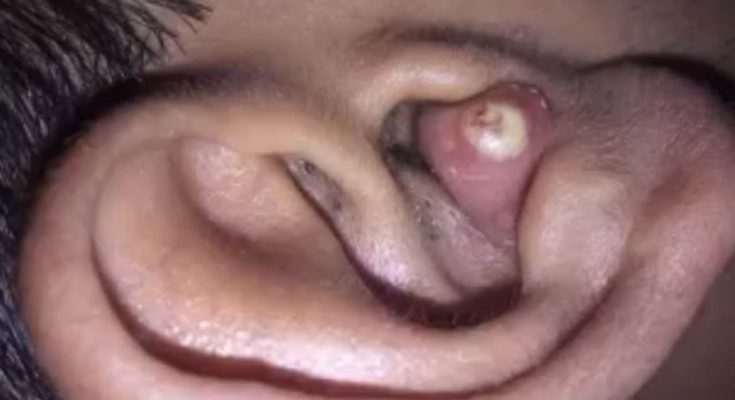
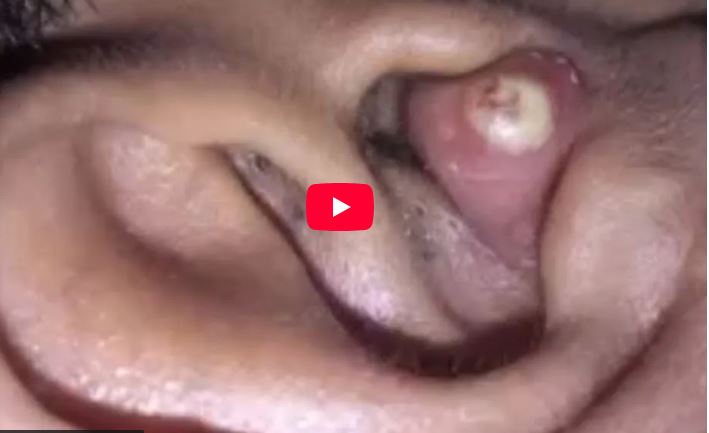
The image shows a close-up of an ear with a swollen, reddish bump inside the ear canal. At the center of the bump, there is a visible white or yellowish point, which appears to be a buildup of pus. This presentation is characteristic of an ear canal abscess or a furuncle, a painful infection that occurs when bacteria invade a hair follicle or the soft tissue within the ear canal. Although small in size, these abscesses can cause significant discomfort due to the sensitivity and limited space inside the ear.
Ear canal abscesses typically begin with irritation—often from scratching inside the ear, inserting cotton swabs, using headphones, or exposure to moisture that encourages bacterial growth. Once bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus enter a small break in the skin, an infection forms. The immune system responds by sending white blood cells, creating pus and inflammation. As pressure builds, the area becomes red, swollen, and increasingly painful, which is clearly visible in the image.
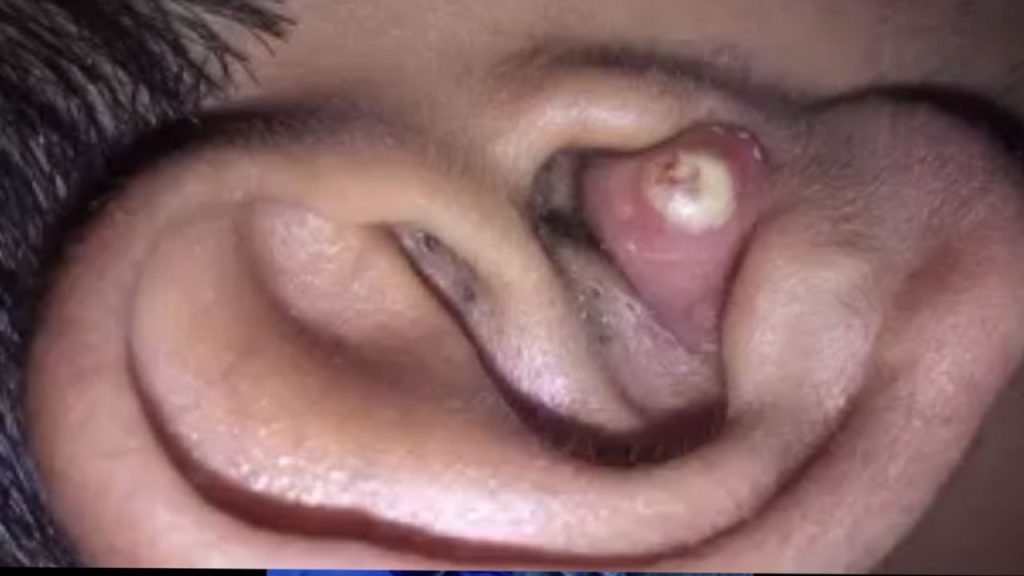
Because the ear canal is narrow, even a small abscess can block sound, cause a feeling of fullness, and potentially affect hearing temporarily. Individuals with this type of abscess may also experience throbbing pain, tenderness when touching the ear, and sometimes mild fever if the infection progresses. If left untreated, the swelling can worsen, the infection may spread, or the abscess can rupture on its own—sometimes painfully and with discharge.
Safe treatment is important. Unlike pimples on the skin surface, ear abscesses should not be squeezed or popped at home because this can worsen the infection, push bacteria deeper, or damage the delicate structures inside the ear. Medical professionals typically treat this condition with warm compresses, prescription antibiotic drops, or oral antibiotics depending on severity. In some cases, a healthcare provider performs a small incision and drainage procedure, which instantly relieves pressure in a controlled, sterile manner.
Daily hygiene also plays a big role in both treatment and prevention. Avoid inserting objects into the ear, even cotton swabs, since these can irritate the tissue or introduce bacteria. For people who frequently experience ear irritation, keeping the ear canal dry and avoiding aggressive cleaning can reduce the risk of future infections. Swimmers, in particular, should dry ears properly to prevent bacterial growth in moist environments.
In conclusion, the image illustrates a small yet painful ear canal abscess with visible pus formation. While such infections are common, they demand proper care to avoid complications. Professional evaluation ensures safe treatment, quicker healing, and prevention of further issues such as hearing disturbance or spreading infection. If someone experiences similar symptoms—especially worsening pain or discharge—seeking medical attention promptly is the safest and most effective approach.