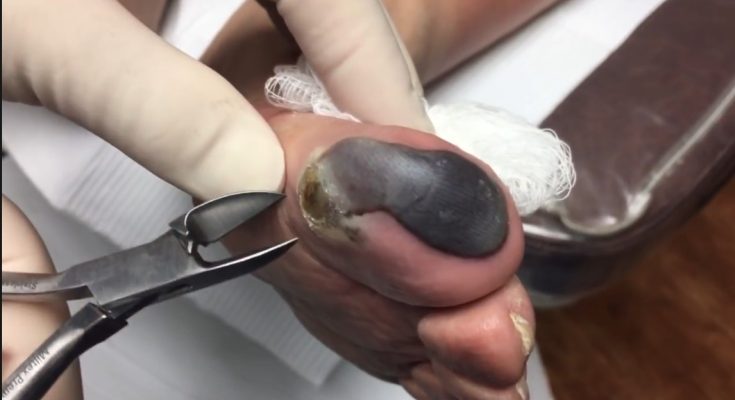
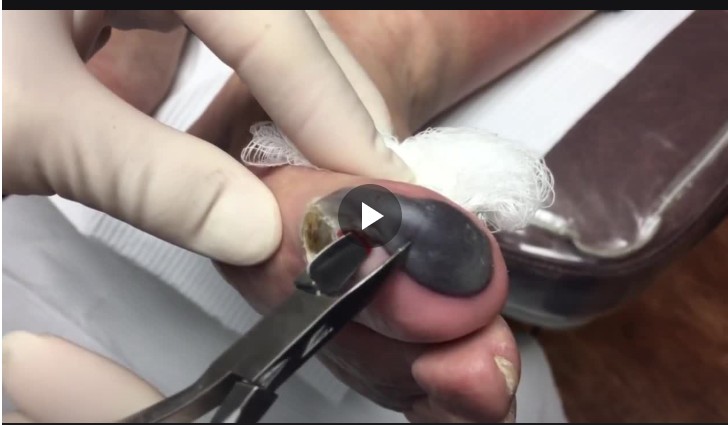
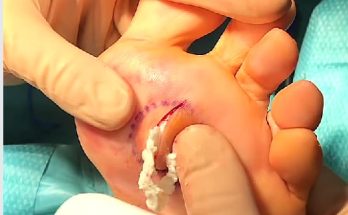
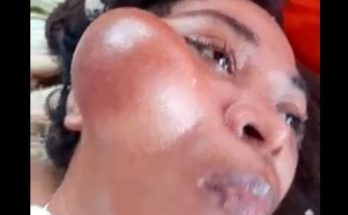
A blood blister on the toe can look alarming — a small, dark red or purple bubble filled with blood under the skin. It may appear suddenly after walking long distances, wearing tight shoes, or experiencing pressure or friction on your foot. While blood blisters can be painful, they are usually harmless and heal naturally over time. Understanding what causes them and how to care for them properly can help prevent infection and speed up recovery.
1. What Is a Blood Blister?
A blood blister forms when the small blood vessels (capillaries) beneath the skin are damaged, causing blood to leak into the space between skin layers. This trapped blood mixes with fluid, creating a raised, red blister. Unlike clear fluid blisters, which are filled with serum, blood blisters contain red blood cells, giving them their distinctive color. The outer skin remains intact, protecting the area from dirt and bacteria while the underlying tissue heals.
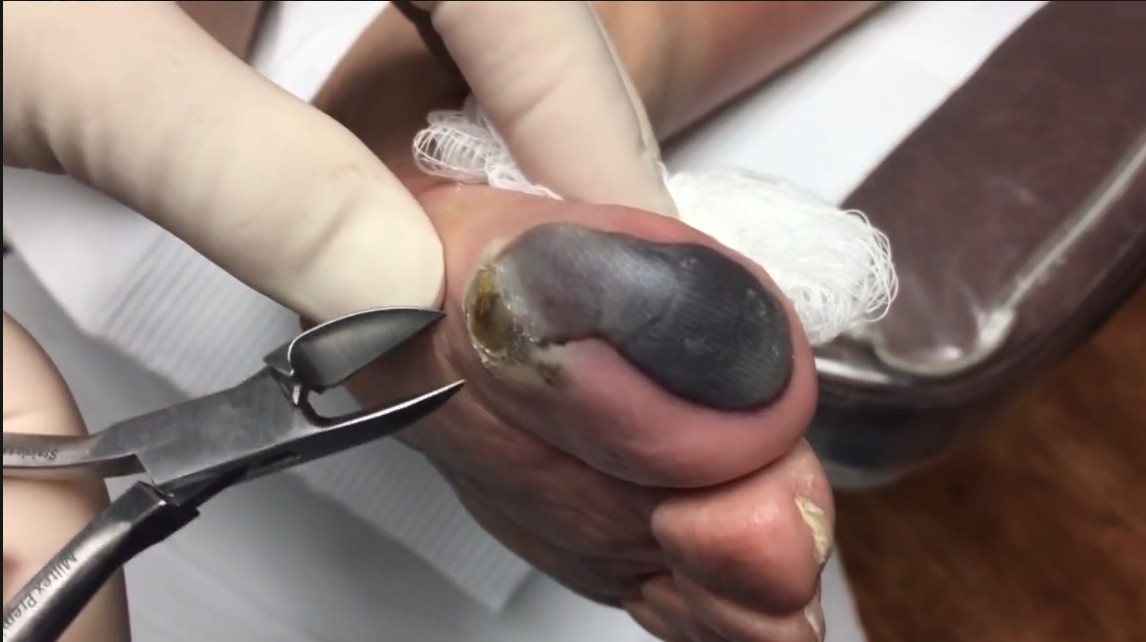
2. Common Causes of Blood Blisters on the Toe
There are several reasons why blood blisters form on the toes, most of which involve pressure, friction, or injury:
-
Tight or ill-fitting shoes: Wearing shoes that are too tight or too loose can cause constant rubbing or pressure on the toes, especially during long walks or exercise.
-
Friction from movement: Activities like running, hiking, or playing sports can cause repetitive friction, leading to irritation and blister formation.
-
Sudden trauma: Accidentally stubbing your toe or dropping something heavy on it can rupture blood vessels and cause a blister.
-
Moisture and heat: Sweaty feet trapped in tight shoes create a warm, moist environment that softens the skin and makes it more vulnerable to blisters.
-
Burns or pinching: Extreme heat, cold, or even pinching injuries can damage the skin enough to cause a blood blister.
3. How the Body Responds
When the skin on your toe experiences pressure or injury, the body reacts immediately by forming a protective fluid pocket. This pocket, filled with blood and serum, cushions the damaged tissue and prevents further friction. It also gives the skin underneath time to regenerate. Over several days, the blister fluid is reabsorbed, and the skin gradually heals on its own.
4. How to Care for a Blood Blister on the Toe
Most blood blisters heal without medical treatment, but proper care helps prevent infection and reduces discomfort. Here’s what you should do:
-
Do not pop the blister: The blister’s outer layer acts as a natural barrier against bacteria. Popping it increases the risk of infection.
-
Keep it clean: Wash your feet gently with mild soap and water.
-
Protect it: Cover the blister with a sterile, non-stick bandage or moleskin to prevent friction.
-
Reduce pressure: Avoid tight shoes or activities that cause rubbing. Wear open-toed or soft footwear until it heals.
-
Cool it down: If painful, apply an ice pack wrapped in a cloth for 10–15 minutes to reduce swelling.
-
Let it drain naturally: If the blister bursts on its own, clean it gently, apply an antiseptic, and cover it with a clean dressing.
5. When to See a Doctor
Most blood blisters heal in one to two weeks, but you should seek medical advice if:
-
The blister is very large or extremely painful.
-
You notice signs of infection, such as pus, redness, warmth, or swelling.
-
You have diabetes or circulation problems, as foot blisters can lead to complications.
-
The blister keeps returning in the same area.
Conclusion
A blood blister on the toe is usually caused by friction, pressure, or minor trauma that damages tiny blood vessels under the skin. Though they may look serious, these blisters are part of the body’s natural healing process. With proper care—keeping the area clean, protected, and free from pressure—most blood blisters heal safely without scarring. To prevent them in the future, wear properly fitting shoes, keep your feet dry, and protect your toes from repeated friction and impact.