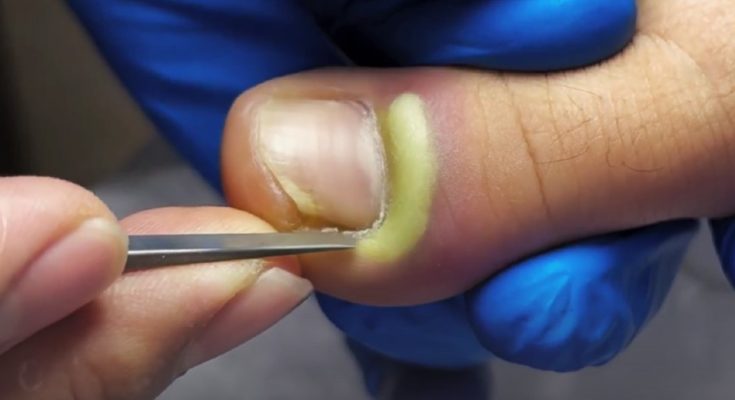
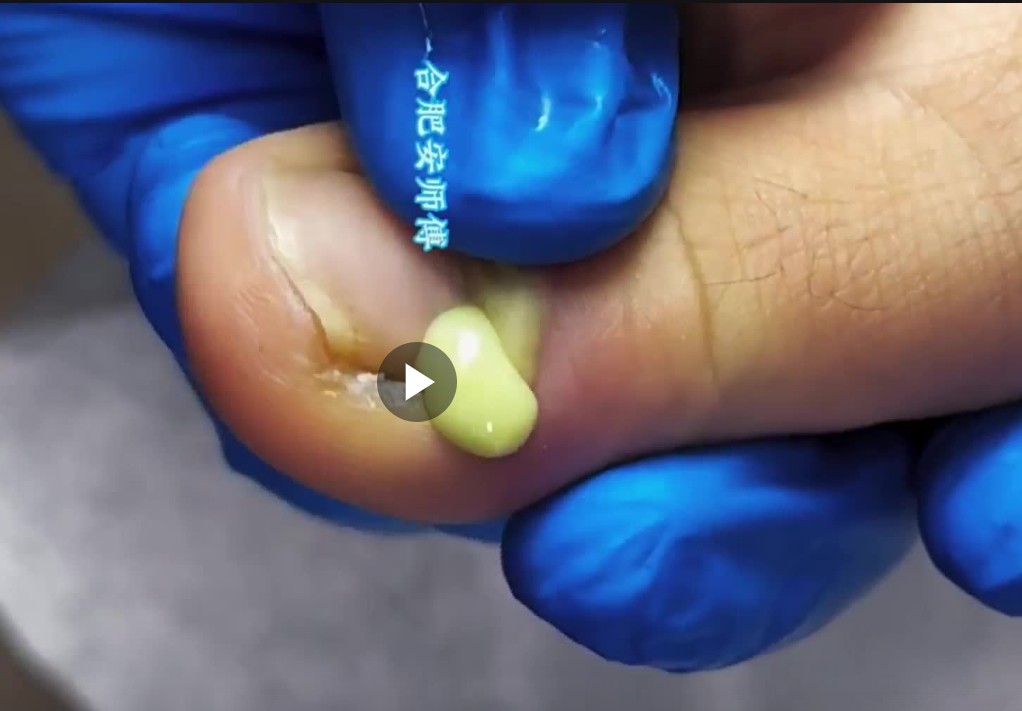
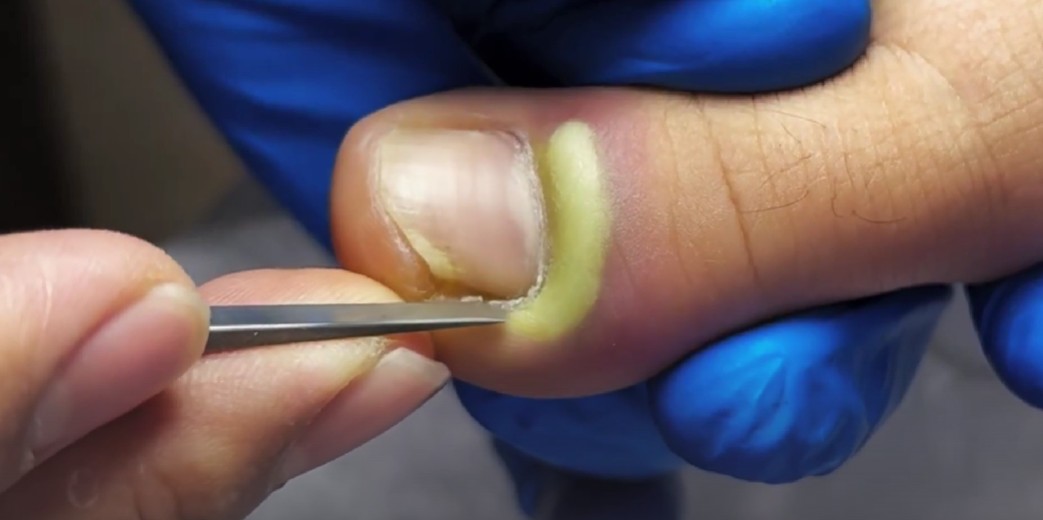
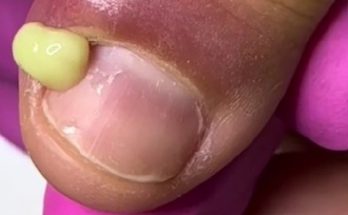
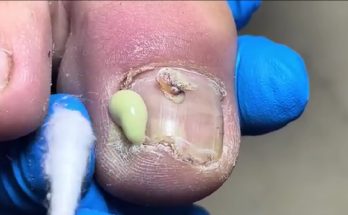
An infected toenail is a common but painful condition that can affect people of all ages. The image above shows a severe toenail infection with visible yellow pus, swelling, and inflammation around the nail bed. This condition is often linked to bacterial infection, ingrown toenails, or poor foot hygiene. If left untreated, it may worsen and lead to serious complications.
What Causes Toenail Infections?
Toenail infections usually occur when bacteria or fungi enter the skin through small cuts, cracks, or improperly trimmed nails. Common causes include ingrown toenails, wearing tight shoes, excessive sweating, nail injuries, and frequent exposure to moist environments. People with diabetes or weak immune systems are at higher risk of developing severe nail infections.
Symptoms to Watch Out For
The most noticeable symptoms include redness, swelling, pain, warmth, and pus discharge around the toenail. In advanced cases, the nail may become thick, discolored, or partially detached from the nail bed. The presence of yellow or green pus, as seen in the image, is a clear sign of bacterial infection and should not be ignored.
Treatment and Care Options
Early treatment is essential to prevent the infection from spreading. Mild infections can sometimes be managed by soaking the foot in warm salt water, keeping the area clean, and applying antiseptic solutions. However, infections with pus often require medical treatment, including antibiotics or professional nail drainage by a healthcare provider.
Avoid squeezing or cutting the infected area at home, as this can worsen the condition. Wearing open or breathable footwear and keeping nails trimmed properly can help speed up recovery.
Prevention Tips
To prevent toenail infections, maintain good foot hygiene, keep nails clean and dry, trim nails straight across, and avoid tight shoes. Regular foot inspections are especially important for people with diabetes.
Conclusion
A pus-filled toenail infection is a serious warning sign that requires prompt attention. With proper care and timely treatment, recovery is possible, and future infections can be avoided. If symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a medical professional is strongly recommended.