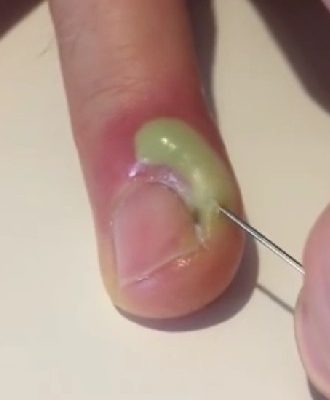
An infected fingernail, also known as paronychia, is a painful condition that develops when bacteria enter the skin around the nail. As seen in the image, pus has formed along the nail edge, indicating an active infection that requires professional medical care.
Fingernail infections often occur due to small cuts, nail biting, aggressive manicures, artificial nails, or trauma to the nail fold. When the protective skin barrier is damaged, bacteria can quickly multiply, leading to redness, swelling, tenderness, and visible discharge. Without proper treatment, the infection may worsen and spread deeper into the nail bed.
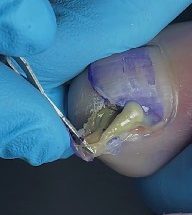
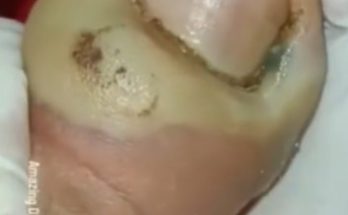
Professional treatment begins with a careful assessment of the affected finger to determine the severity of the infection. The area is cleaned thoroughly under sterile conditions to prevent further contamination. Using precise medical instruments, the clinician gently opens the infected area to allow trapped pus to drain. Controlled drainage is essential to relieve pressure, reduce pain, and promote faster healing.
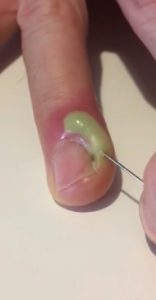
Once the infection is drained, the nail and surrounding skin are cleaned again to remove bacteria. Depending on the extent of the infection, topical or oral antibiotics may be recommended to support recovery. Early intervention helps protect the nail structure and prevents permanent nail damage or recurrent infections.
Proper aftercare is a key part of the healing process. Patients are advised to keep the finger clean and dry, avoid nail trauma, and follow all medical instructions provided by the clinician. Activities that place stress on the nail should be limited until healing is complete.
Seeking professional care for fingernail infections ensures safe treatment and reduces the risk of complications. If you experience finger pain, swelling, redness, or pus near the nail, prompt medical attention can restore comfort and protect long-term nail health.