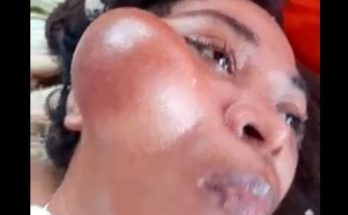
A massive ear abscess is a painful and serious condition that develops when an infection causes a buildup of pus inside or around the ear. Because the ear contains delicate structures and is close to important nerves, any swelling in this area should be taken seriously. When the abscess grows large, it can cause intense discomfort, pressure, and difficulty moving the surrounding tissues. In many cases, incision and drainage performed by a medical professional is the most effective and safest treatment method. Understanding why ear abscesses form, how the procedure works, and what to expect afterward is essential for proper care and recovery.
An ear abscess typically begins with a bacterial infection. This can occur after a blocked pore, an infected hair follicle, an insect bite, or damage from scratching the skin. People with ear piercings, eczema, or chronic ear infections are at higher risk of developing abscesses. When bacteria enter the skin, the immune system responds by sending white blood cells to fight the infection. As these cells accumulate, pus forms, creating an abscess. If the infection is not treated early, the swelling may grow larger and become increasingly painful.
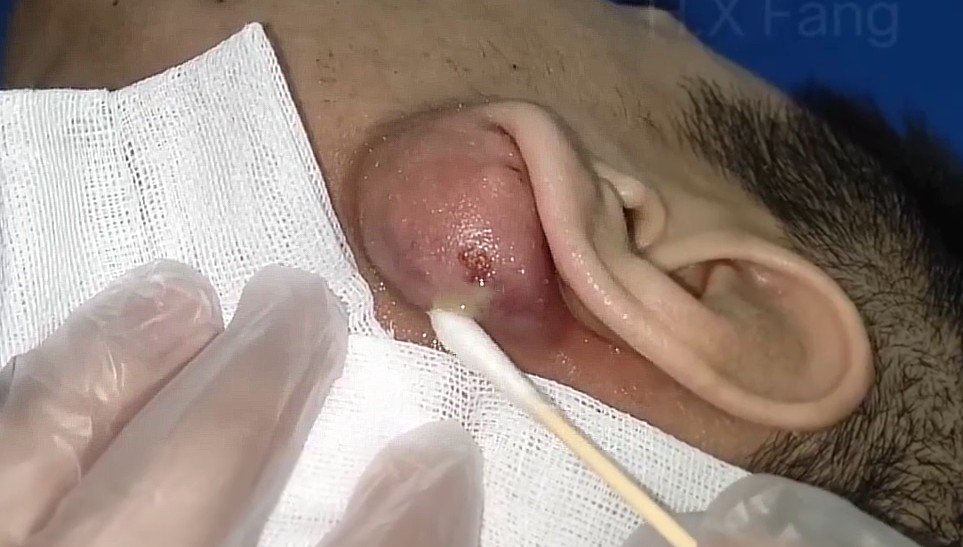
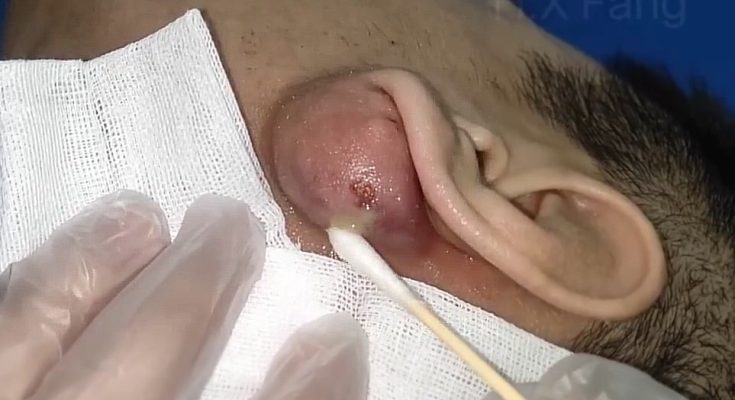
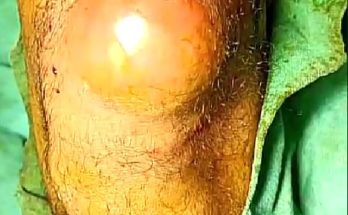
Symptoms of a massive ear abscess include redness, swelling, warmth, tenderness, and noticeable pressure around the affected area. The skin may feel tight or stretched, and the person may experience difficulty sleeping on that side. In more severe cases, fever, throbbing pain, or difficulty hearing can occur. Because the abscess is located close to the ear canal and inner ear structures, prompt treatment is important to prevent the infection from spreading.
Incision and drainage is the most reliable treatment when the abscess becomes large. The procedure is performed by a healthcare professional to ensure safety and proper infection control. Before beginning, the doctor examines the area to confirm the exact location and size of the abscess. The skin is then cleaned thoroughly with antiseptic solution to minimize the risk of spreading bacteria. Local anesthesia is usually applied to numb the area, making the procedure more comfortable.
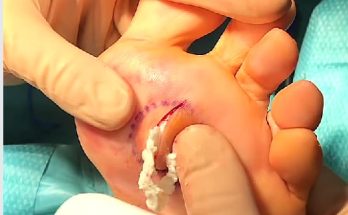
Once the area is numb, the doctor makes a small, precise incision over the swollen area. This allows the trapped pus to drain out safely and reduces the pressure that causes pain. As the fluid is released, patients often feel immediate relief. After drainage, the doctor may gently flush the cavity with sterile solution to remove any remaining debris. In some cases, a small piece of medical gauze or a soft drain may be inserted temporarily to ensure the abscess continues to empty and does not close too early.
After the procedure, patients are typically prescribed antibiotics to eliminate the infection completely. Pain relievers may also be recommended during the first few days of recovery. Keeping the area clean and dry, avoiding touching or scratching the ear, and following the doctor’s instructions are important for proper healing. Warm compresses may help reduce remaining discomfort.
Preventing ear abscesses involves good hygiene and proper skin care. Avoiding excessive scratching, keeping the ears clean, and treating minor skin irritations early can significantly reduce the risk. Those with ear piercings should ensure proper aftercare to prevent infections.
In summary, a massive ear abscess incision and drainage procedure is a safe and effective way to relieve pain, eliminate infection, and promote healing. With proper medical care and aftercare, most patients recover quickly and comfortably.