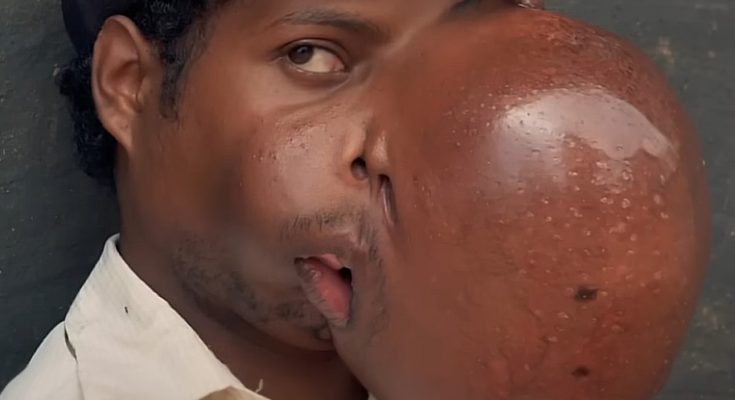
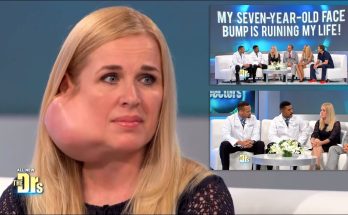
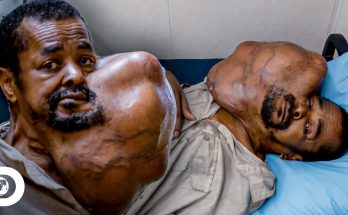
Tumor on the Face: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
A tumor on the face can be an alarming and distressing condition, not only because it affects appearance but also because it may indicate an underlying health issue. A tumor is an abnormal growth of cells that can develop anywhere in the body, including the skin, muscles, or bones of the face. While most facial tumors are benign (non-cancerous), some can be malignant (cancerous) and require immediate medical attention. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for facial tumors is essential for proper care and peace of mind.
Causes of Facial Tumors
Facial tumors can develop for various reasons, depending on the type of cells involved. The most common causes include genetic mutations, which cause cells to grow uncontrollably. Environmental factors, such as sun exposure, radiation, or contact with harmful chemicals, can also increase the risk of tumor development. In some cases, chronic inflammation, infection, or trauma to the skin may contribute to abnormal cell growth.
Benign facial tumors often result from blocked glands or tissue overgrowth, such as sebaceous cysts, lipomas (fatty lumps), or fibromas. These types of tumors are usually soft, movable, and slow-growing. On the other hand, malignant tumors, such as skin cancer or sarcoma, tend to grow rapidly, invade nearby tissues, and sometimes spread to other parts of the body.
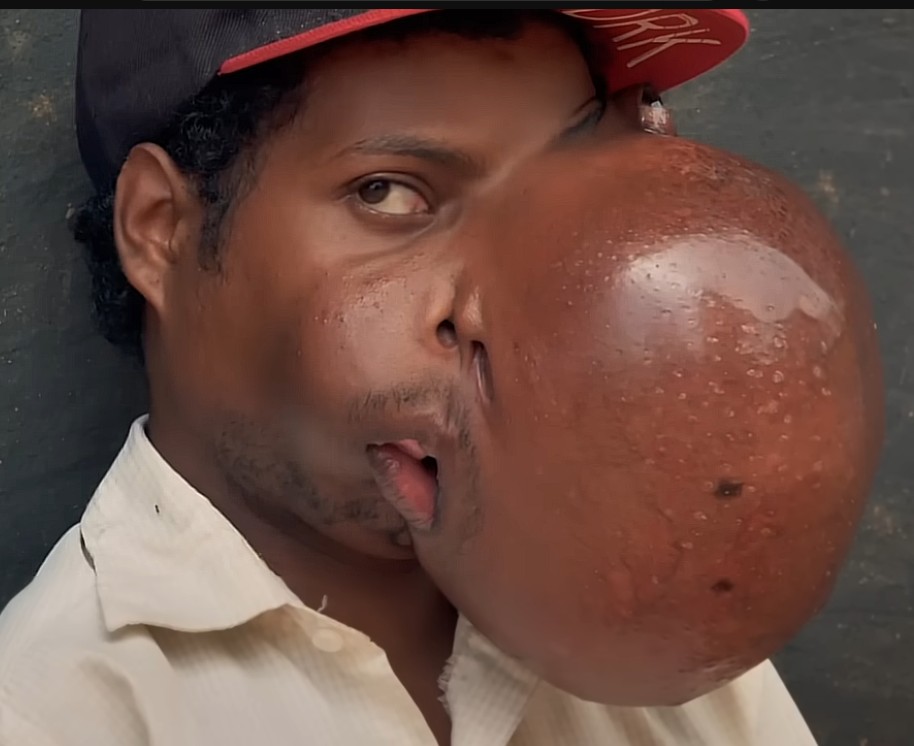

Symptoms of a Facial Tumor
The symptoms of a tumor on the face depend on its size, location, and nature. Common signs include a visible lump or swelling, pain or tenderness in the affected area, and changes in skin color or texture. Some tumors may cause numbness, bleeding, or ulceration if they grow near nerves or break through the skin’s surface.
If a tumor presses on facial muscles or nerves, it can lead to difficulty moving parts of the face or asymmetry. In some cases, malignant tumors can cause weight loss, fatigue, or swollen lymph nodes. Because these symptoms can resemble those of other skin conditions, it is essential to get a proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional.
Diagnosis and Treatment
When a facial tumor is detected, doctors usually begin with a physical examination and medical history. Imaging tests such as MRI, CT scans, or ultrasound may be used to determine the tumor’s size and depth. A biopsy, where a small tissue sample is taken and examined under a microscope, is often performed to determine whether the tumor is benign or malignant.
Treatment depends on the diagnosis. Benign tumors may only require surgical removal if they cause discomfort or cosmetic concern. The procedure is typically simple and done under local anesthesia. Malignant tumors, however, often require more aggressive treatment, such as surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or targeted medication to eliminate cancer cells and prevent recurrence.
Prevention and Care
To reduce the risk of developing facial tumors, it’s important to practice sun protection, such as using sunscreen, wearing hats, and avoiding excessive UV exposure. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, eating a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco can also lower your risk. Regular self-checks and medical examinations can help detect any unusual lumps early.
In conclusion, a tumor on the face can vary from a harmless cyst to a serious medical condition. Early detection and professional evaluation are the keys to successful treatment. Whether benign or malignant, addressing a facial tumor promptly ensures better outcomes and helps maintain both health and confidence.